修改界面,在顶部横条上增加一个添加按钮,点击打开一个自定义对话框,输入电话号码和拦截模式保存到数据库
自定义对话框看这篇http://www.cnblogs.com/taoshihan/p/5370378.html

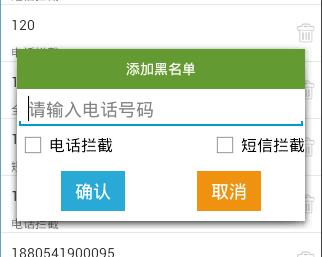
添加记录
调用Builder对象的show()方法,获取AlertDialog对象
调用View.inflate()方法,将布局文件转成View对象
调用View对象的findViewById()方法,获取确认和取消的Button对象
调用Button对象的setOnClickListener()方法,设置点击事件,匿名内部类实现OnClickListener接口,重写onClick()方法
调用AlertDialog对象的dismiss()方法,可以关闭对话框
调用View对象的findViewById()方法,获取到各个控件的值,进行判断处理
调用之前定义好的Dao类BlackNumberAdo对象的add()方法,数据库增加一条记录,参数:String电话号码,String拦截模式
此时ListView并不会显出出来刚添加的记录,需要退出这个Activity重写进入,我们通知适配器数据更新
调用集合List对象的add()方法,添加一条数据,参数:0(第一个),数据
调用ListAdapter对象的notifyDataSetChanged()方法,通知数据更新
删除记录
条目布局文件中,在右侧放置一个垃圾桶的小图标,上下居中,父控件右边
安卓系统的点击事件和js的点击事件很相似,
参考这篇:
获取到删除按钮Button对象
调用Button对象,设置点击事件
获取AlertDialog.Builder对象,展示是否确认删除的对话框
调用AlertDialog.Builder对象,设置确认按钮和取消按钮,注意设置点击事件OnClickListener时,它所在的包是DialogInterface.OnClickListener
调用之前定义好的Dao类BlackNumberAdo对象的delete()方法,参数:String电话号码
调用集合List对象的remove()方法,删除一条数据,参数:int索引
调用ListAdapter对象的notifyDataSetChanged()方法,通知数据更新
CallSmsSafeActivity.java
package com.qingguow.mobilesafe;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.List;import java.util.Map;import android.app.Activity;import android.app.AlertDialog;import android.app.AlertDialog.Builder;import android.content.DialogInterface;import android.os.Bundle;import android.text.TextUtils;import android.view.View;import android.view.View.OnClickListener;import android.view.ViewGroup;import android.widget.BaseAdapter;import android.widget.Button;import android.widget.CheckBox;import android.widget.EditText;import android.widget.ImageView;import android.widget.ListView;import android.widget.TextView;import android.widget.Toast;import com.qingguow.mobilesafe.db.ado.BlackNumberAdo;/** * 通讯卫士 * * @author taoshihan * */public class CallSmsSafeActivity extends Activity { private ListView listview; private List

